Gas Sensor Cross Sensitivity
June 11, 2019
Updated: September 26, 2022
This article describes gas cross sensitivity, how it can impact your gas sensors, and what gas sensors can exhibit it. The article applies to G7c, G7x, and G7 EXO.
What is gas sensor cross sensitivity?
Cross sensitivity is a phenomenon that occurs when a gas other than the gas being monitored causes the gas sensor to show a reading, even when the target gas is not present. An example of this would be an H₂S sensor responding to H₂ in the area.
What does Blackline do to alleviate cross sensitivity?
To alleviate cross sensitivity, Blackline:
- Chooses sensors that are less likely to show a cross sensitive response
- Includes filtration to remove the cross sensitive gases
- Tests sensor and gas combinations to confirm the cross sensitive responses to other gases
What will I see During Calibration or Bump Testing when sensors are cross sensitive?
During calibration and bump testing a cross sensitive sensor, you will see readings on the sensor you are not calibrating or bump testing because the sensor has a response to the gas being applied during the calibration or bump testing.
What can I do when sensors get cross sensitive readings?
To reduce these cross sensitive responses, Blackline strongly recommends following the prescribed order of the gases applied to the device when doing either Dock or manual calibration or bump testing. For most sensor/gas combinations, the cross sensitive response can be removed by exposing the device to fresh air. Please consult with Customer Care for recommended fresh air exposure times.
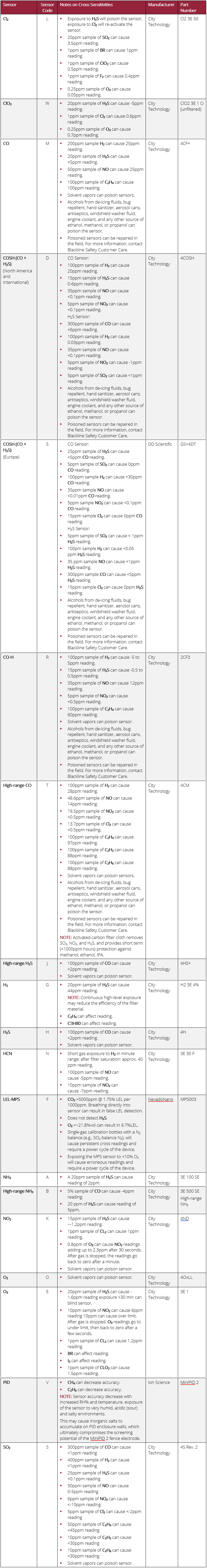
What gas combinations produce noticeable cross sensitivity?
Almost all gases cause some cross sensitivity, but our devices are designed to filter out many of the most commonly occurring ones.
The following sensors can have cross sensitivity.
We’re here to help
Let us know if you have any questions — don’t hesitate to reach out to our Customer Care team.